
Hence the assumption of the development of uniform bond stress along the anchorage length is used to calculate anchorage lengths of bars regardless of the variations in anchorage lengths or bar diameter. It is also observed that lap splice length (ls) decreases when the concrete strength (f’c) increases.Īnalysis and design provisions for the bond and anchorage length of deformed reinforcing bars in reinforced concrete elements are typically developed based on the assumption that the strain variations along the bar becomes approximately linear at or near the ultimate state of bond failure. It is also found from that bars of higher yield strength (f¬y) requires larger lap splice length (ls). AASTHO and BNBC design codes also exhibit same splice length for 36 mm Φ bar or smaller. Lap splice length (ls) increases when the bar diameter (d¬b) increases. AASTHO and BNBC design codes recommend smaller lap splice lengths (ls). CEB - FIP MODEL recommends larger splice length for larger bars than 12mm Φ bar.
LAP SPLICE TABLE CODE
After analyzing the sample calculations and graphs it is concluded that among all codes, ACI code recommends the larger splice length for12mm Φ bar. In this thesis parametric study was performed where compressive strength of concrete (f’c), yield strength of the reinforcing bars (fy) and bar diameters were the parameter. In this study we reviewed ACI (2002), BNBC (1993), AASHTO (2007), CEBFIP Model (1990) and EURO Code 2(2003) design codes and compared the variation of lap splice length. Various design codes have provided many laws to calculate lap splice length. In this study tension and contact lap splices are considered. Non-contact lap-spliced bars should not be spaced too far apart. Contact splices in which the bars touch and are wired together are preferred because they are more secure against displacement during construction.

One is contact and the other one is non contact. The length of the lap varies depend on concrete strength, the rebar grade, size, and spacing. A lap is when two pieces of rebar are overlapped to create a continuous line of rebar. Properly designed splices are a key component in a well-executed design. Splices of reinforcing bars are unavoidable.
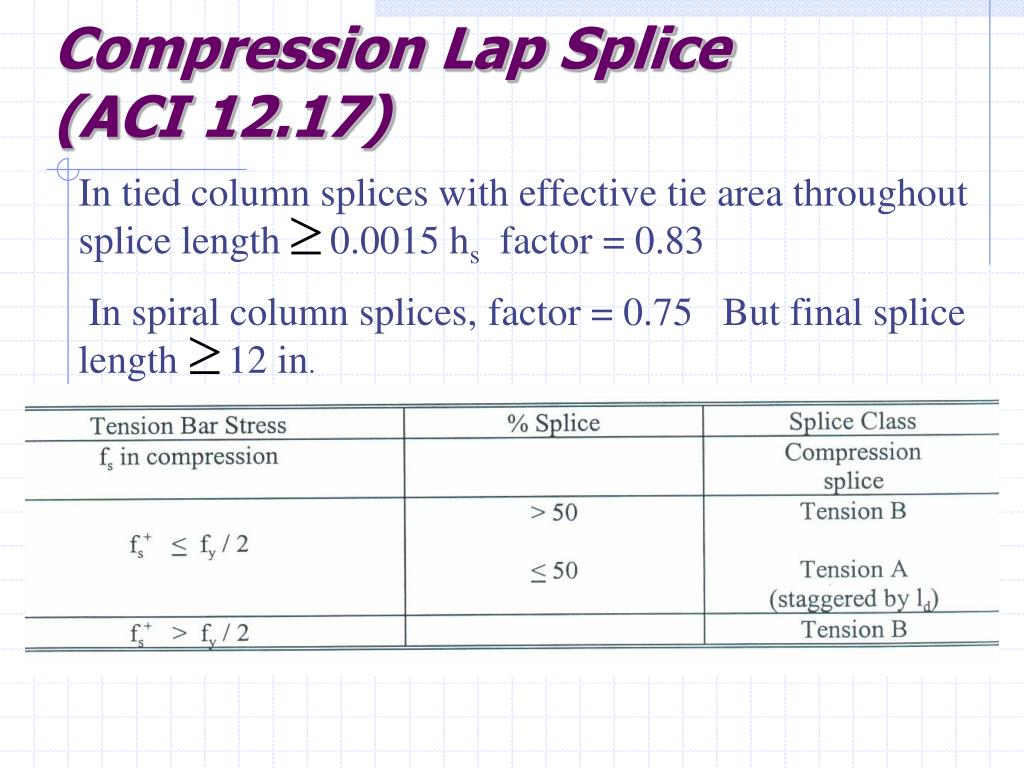
Just as it is physically impossible to place all concrete in one continuous operation, it is impossible to provide full-length, continuous reinforcing bars throughout any sizeable structure. Due to practical limitations, the actual structure must be built piece-by-piece, story-by-story, and connected together.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
